A friend of mine came across to me and asked me: Hey man Have you installed ORDS in a multitenant environment?
Short answer: YES, I did (some time ago)
And there is a lot of documentation available online, so let’s add more info and create this post about it, right?. Just to clarify in this post my setup will be the following:
Setup:
- Oracle REST Data Services 23.2.3
- Oracle Database 23c FREE
- CDB: FREE
- PDB: FREEPDB1
- CDB: FREE
ORDS Installation
I have already an Oracle 23c database running in my local VM, so I’m going to focus on the ORDS installation only, let’s go!
So, first at all you can download ORDS software from here: ORDS
I have already done that and the software is located in the home of the Oracle user, for the purpose of this demo I’m going to create a folder for the ORDS software in the following path: /opt/ords/23.2.3
Folder is created and oracle user is the owner:

Nice! Let’s unzip the ords software:
unzip -d /opt/ords/23.2.3/ ords-23.2.3.242.1937.zip
As you can see below, software is unzipped and we can proceed with the next steps
Let’s setup ORDS:
From folder: /opt/ords/23.2.3/bin let’s run the ords binary to perform the installation with the following command:
./ords --config /opt/ords/config install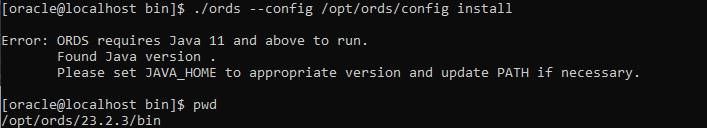
Note two things:
- I haven’t set JAVA_HOME yet
- I will create all my configuration files under directory: /opt/ords/config
If you don’t have Java installed (I haven’t, for example), you can download it from here: Java download
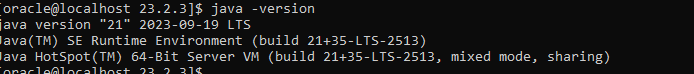
I have installed JAVA and it is set in my PATH environment, let’s try again:
So, couple of things, the installation asked me for:
- Type of installation
- Database connection details, in this example I have my Oracle 23c Free database running locally, so I have provided the basic details: host, port of my listener and the service_name
- Administrator username, in this case SYS
- Password for Administrator username, in this case SYS
The installation connects to the database and creates a common user in the CDB$ROOT container: ORDS_PUBLIC_USER. The ORDS schema is also created/installed in the PDBs, including the PDB$SEED as it is internally opened in READ/WRITE mode. So, you can create PDBs from the SEED in the future that will include ORDS configured!
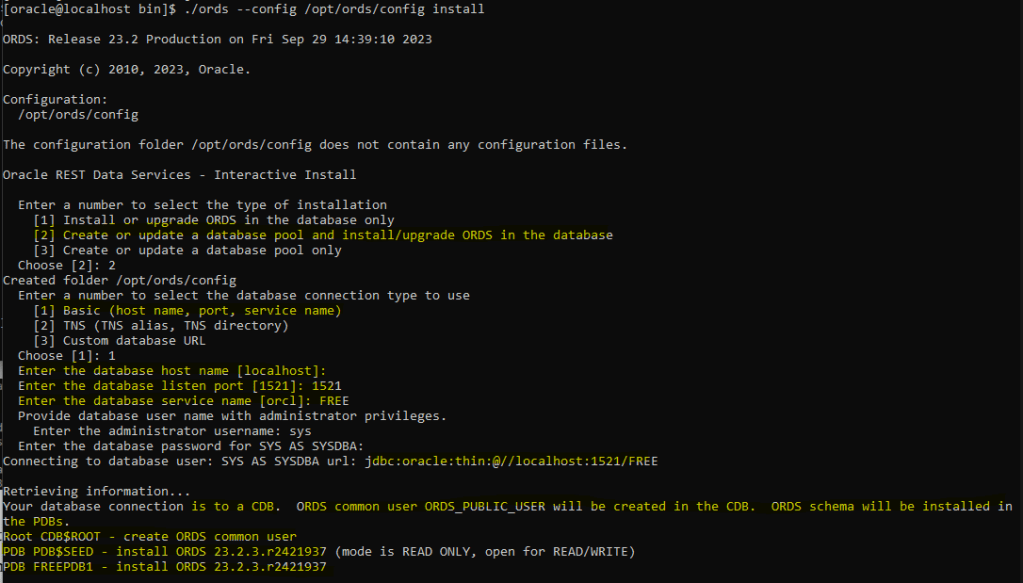
Ok, so it asks to confirm the installation for ORDS in the database and for tablespaces to create the objects. The default is SYSAUX as the permanent tablespace and TEMP for the temporary tablespace. For a proper installation in a production environment, make sure to use another tablespace.
Ok, let’s move on. I have selected in the database actions to include all the features, I want to configure and start ORDS in standalone mode listening on port 8080 in HTTP.
It is recommended to use HTTPS with a proper SSL certificate in a PROD environment.
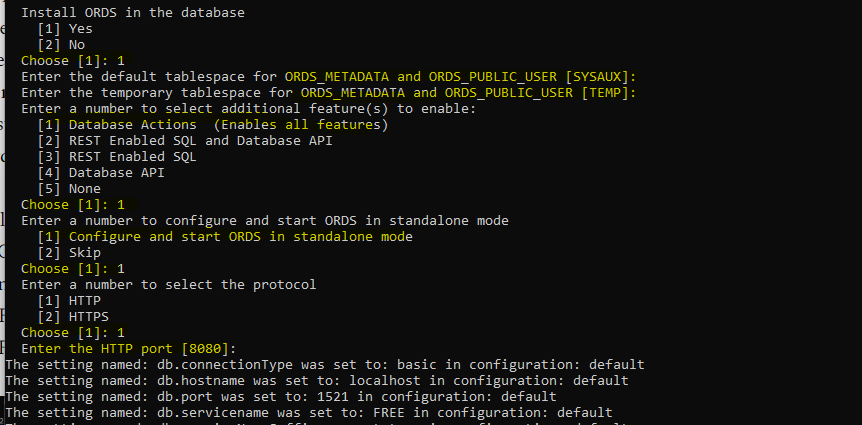
Installation is completed!
START ORDS
ORDS got started automatically after installation, but I did stop it so I can show you how to do it.
To start ORDS you can run the following command considering that you have saved all your configuration in the following path /opt/ords/config, make sure to change it if you use another one:
[oracle@localhost bin]$ pwd
/opt/ords/23.2.3/bin
[oracle@localhost bin]$ ./ords --config /opt/ords/config serve
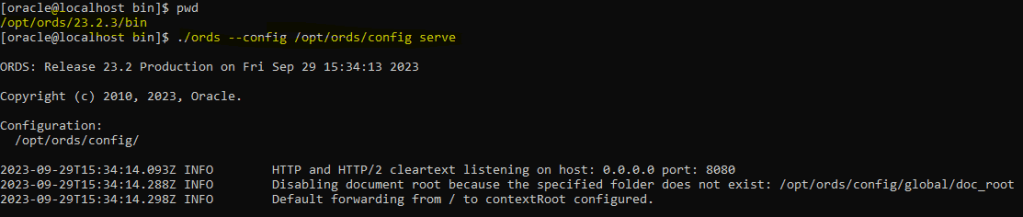
ORDS is running!
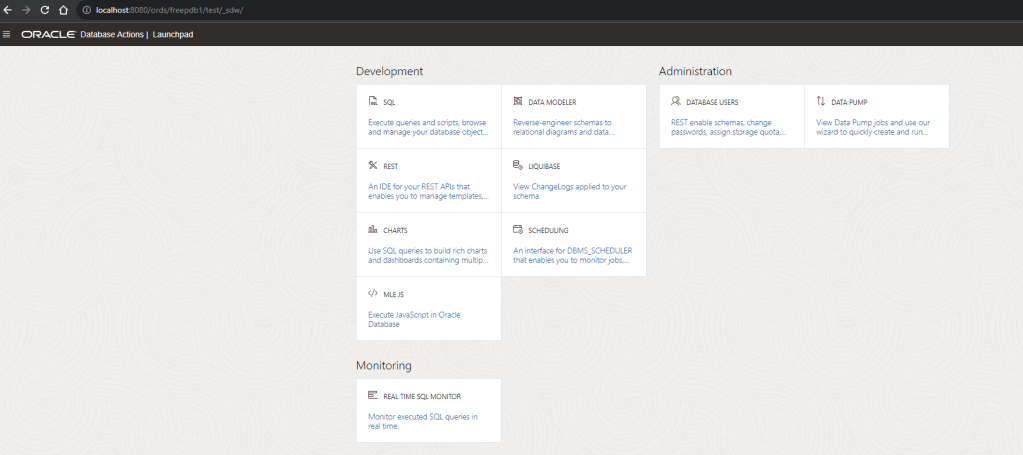
Let’s take a look and access to localhost on port 8080
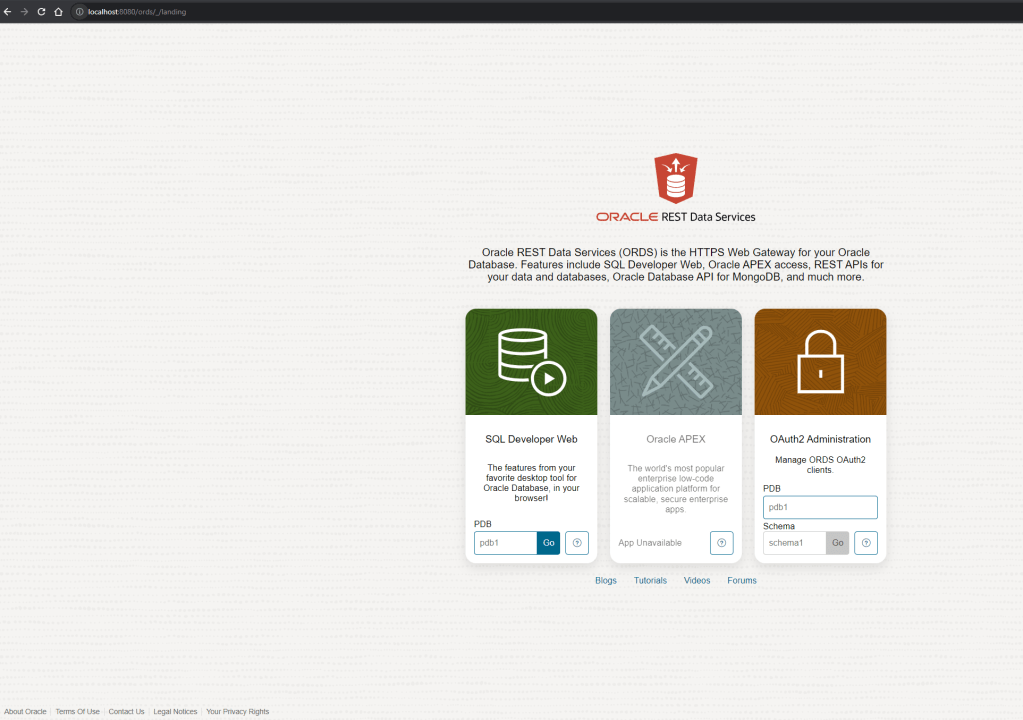
Great, we can see the UI!
Now, how can I connect?
Connect to ORDS
We need to enable REST web services for a schema, I will use the following user: TEST_ORDS.
It is recommended to use an alias for the user in order to not expose the schema name in the URL mapping, for this case as this is an example I will use: TEST only.
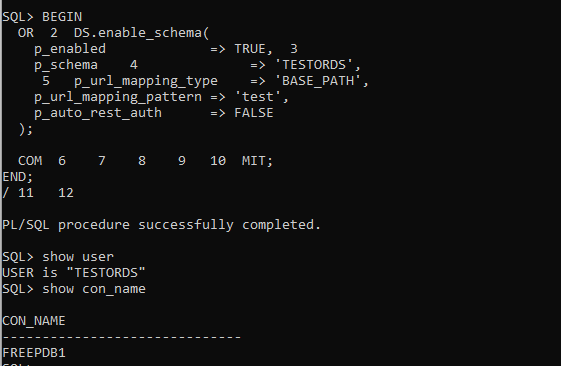
DECLARE
PRAGMA AUTONOMOUS_TRANSACTION;
BEGIN
ORDS.ENABLE_SCHEMA(
p_enabled => TRUE,
p_schema => 'TESTORDS',
p_url_mapping_type => 'BASE_PATH',
p_url_mapping_pattern => 'test',
p_auto_rest_auth => FALSE);
commit;
END;
/Let’s connect with TEST_ORDS in the PDB and run the command:
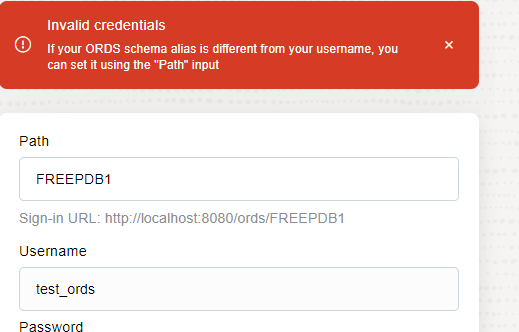
Let’s try to connect using the UI now. Please note that I will connect to a PDB instead of a non-CDB database. I need to provide the PDBNAME and user alias in the path; otherwise, it will fail like the example below:
Good connection:
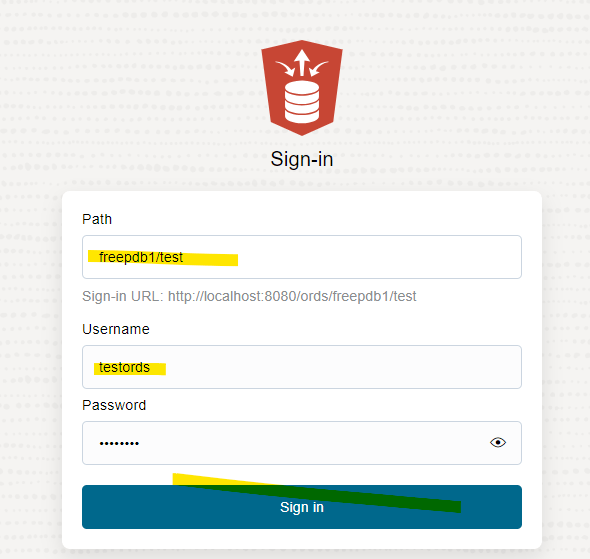
And I’m in!



Leave a comment